The Evolution of the Internet and World Wide Web: From Inception to the Digital Age
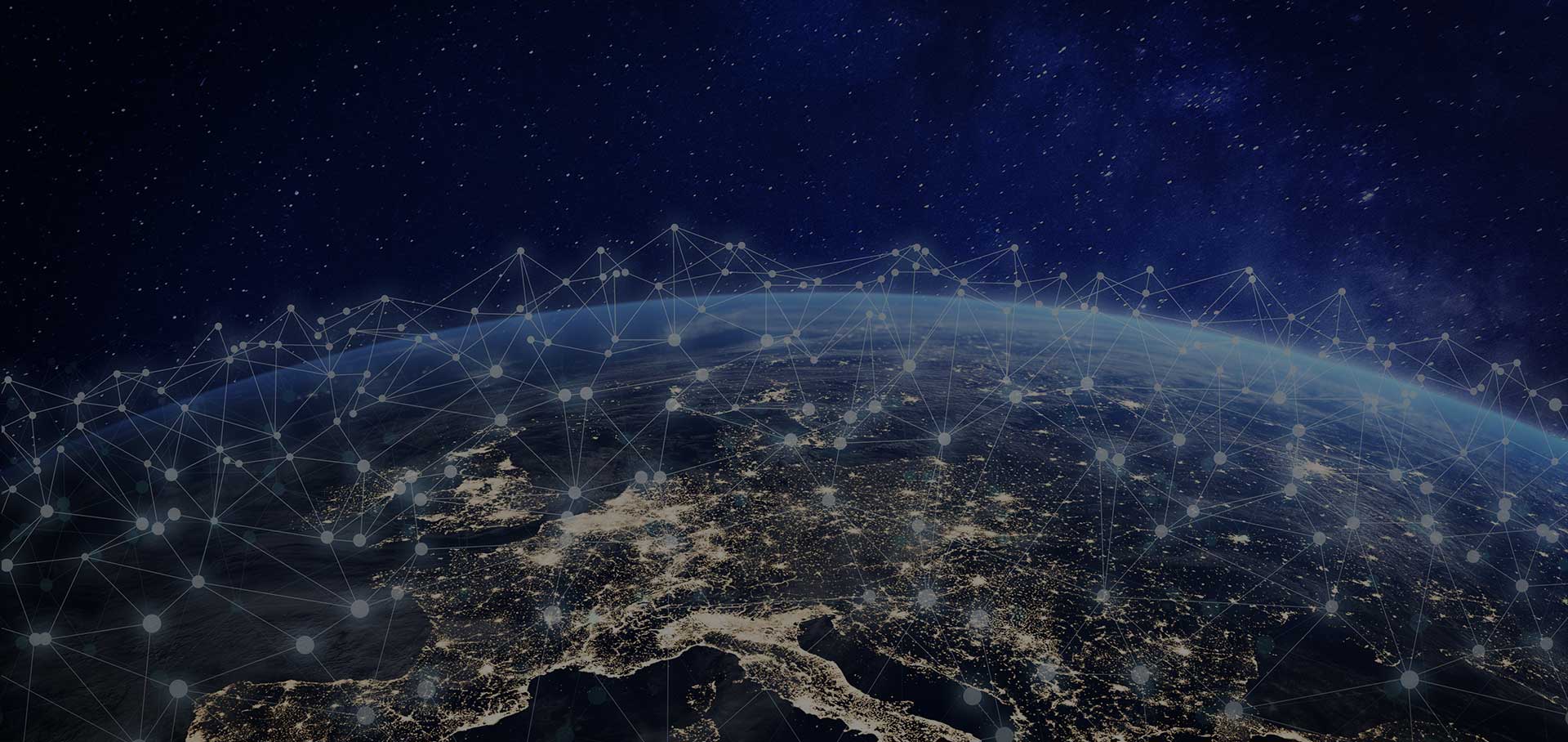
In the modern digital era, the terms “internet” and “World Wide Web” have become synonymous with our daily lives, revolutionising communication, commerce, and information exchange.
But how did it all begin, and how has this technological marvel evolved to shape our world today? Let’s embark on a journey through time, exploring the creation and history of the internet and the World Wide Web.
Birth of the Internet:
The story of the internet traces back to the late 1960s during the height of the Cold War. The United States Department of Defence’s Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) conceived a network of computers that could communicate and share information even in the event of a catastrophic event, a concept that laid the foundation for what we now know as the internet.
In 1969, ARPANET, the first network to implement the TCP/IP protocol suite, was born. This groundbreaking development allowed computers to connect and communicate regardless of their hardware or software differences. ARPANET’s success led to the rapid expansion of computer networks, giving rise to the interconnected digital landscape we rely on today.
The World Wide Web Emerges:
While the internet laid the groundwork for global connectivity, it was the invention of the World Wide Web that truly democratised information access. In 1989, British computer scientist Sir Tim Berners-Lee envisioned a system that would allow users to easily access and share documents over the internet. This vision materialised in 1991 when Berners-Lee released the first web page, outlining the principles of the World Wide Web.
The World Wide Web introduced concepts like URLs (Uniform Resource Locators), HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol), and HTML (Hypertext Markup Language), which made it possible to create and navigate web pages. With the release of the Mosaic web browser in 1993, the web became more user-friendly and visually engaging, setting the stage for its explosive growth.
The Dot-Com Boom and Beyond:
The mid-1990s witnessed the dawn of the dot-com era, characterised by a rapid influx of internet-based businesses and a surge in web usage. Companies like Amazon, eBay, and Yahoo became household names, showcasing the internet’s potential for e-commerce, online auctions, and information dissemination.
The 2000s saw the rise of social media platforms like Friendster, MySpace, and eventually Facebook, forever changing how we connect and communicate. Search engines like Google revolutionised information retrieval, and the advent of smartphones brought the internet into the palms of our hands.
The Internet of Things and Beyond:
As we entered the 21st century, the internet’s influence expanded beyond computers and smartphones. The concept of the Internet of Things (IoT) emerged, connecting everyday objects to the internet and enabling seamless data exchange. Smart homes, wearable devices, and interconnected appliances became part of the growing IoT ecosystem.
Today, we stand at the threshold of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, characterised by artificial intelligence, big data, and the integration of digital technologies into every aspect of our lives. High-speed internet connections, fibre-optic networks, and 5G technology have further accelerated the internet’s transformative power.
Conclusion:
From its humble origins as a military project to its present-day ubiquity, the internet and the World Wide Web have profoundly shaped human society. What began as a means of communication has evolved into a global network that connects individuals, businesses, and governments across the world. As we look to the future, the internet’s continued evolution promises even greater innovation and connectivity, ushering in new possibilities and opportunities for generations to come.
In this era of rapid technological advancement, we can only imagine the extraordinary developments that lie ahead, fuelled by the relentless drive to expand our digital horizons and explore the boundless potential of the internet and the World Wide Web.